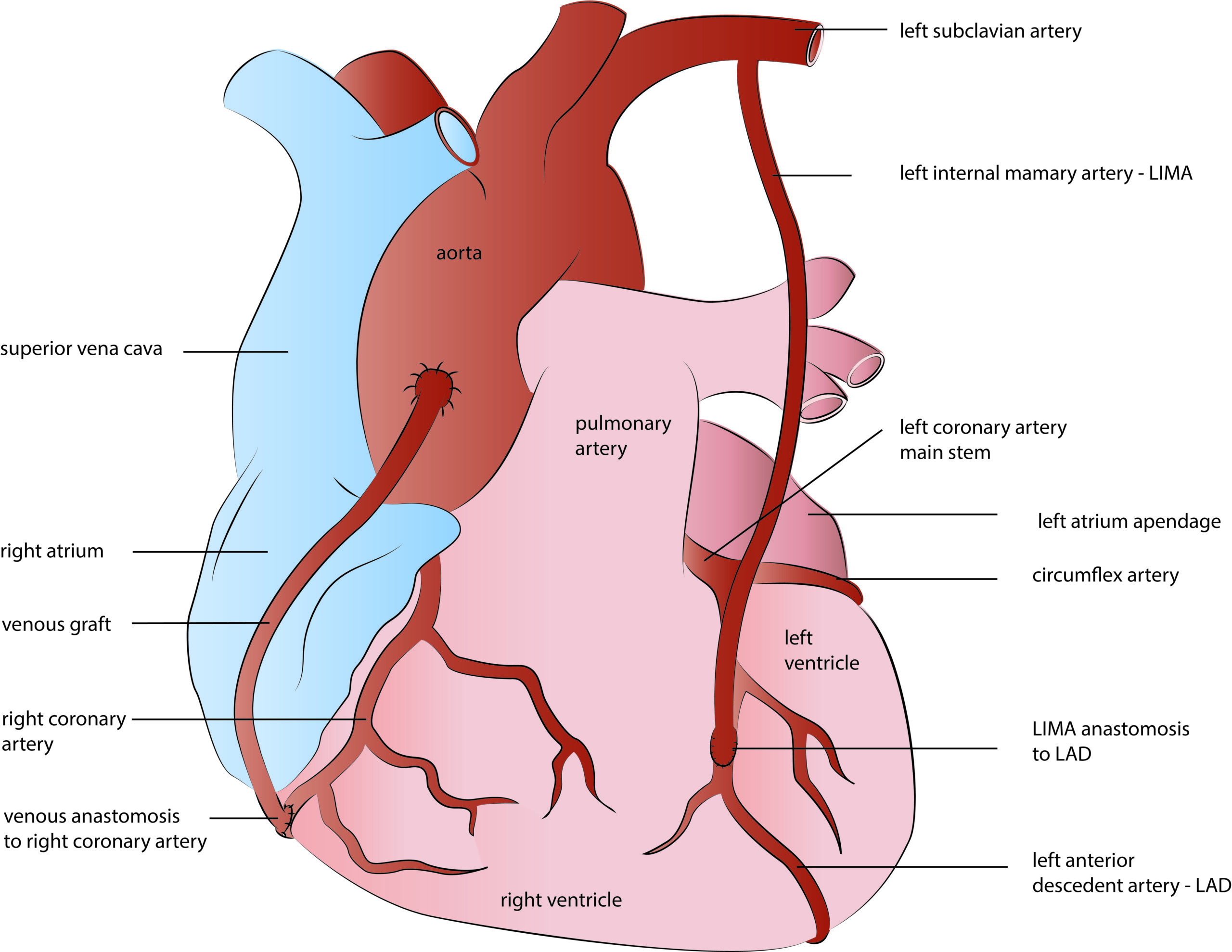
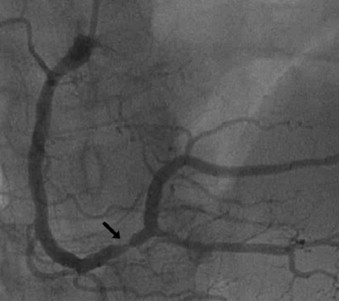
There are two types of blood vessels or grafts used for coronary bypasses: arterial and venous. Venous grafts are harvested from the so-called great saphenous vein, which is a superficial vein from inside your leg. Due to wall anatomy and histology, vein grafts are of inferior quality and, therefore, less durable than arterial grafts. In contrast, arterial grafts are long-lasting and provide superior life quality and long-term survival. Left internal mammary artery – LIMA, is the most commonly used arterial graft. It is harvested from inside of the chest wall and generally used for the left anterior descendent coronary artery bypass. Due to the excellent long-term results, LIMA became a gold standard in coronary surgery today, providing more than 90 % of graft patency rate in the long term follow up studies.
Apart from LIMA, other arteries like right mammary or radial artery- RIMA, are used in coronary surgery today, providing either multiple or total arterial heart revascularization (TAR). The radial artery is a forearm blood vessel frequently used in younger patients as a graft for CABG surgery. Of course, the collateral forearm arteries are previously tested if capable of providing adequate blood supply to hand once the radial artery harvesting.